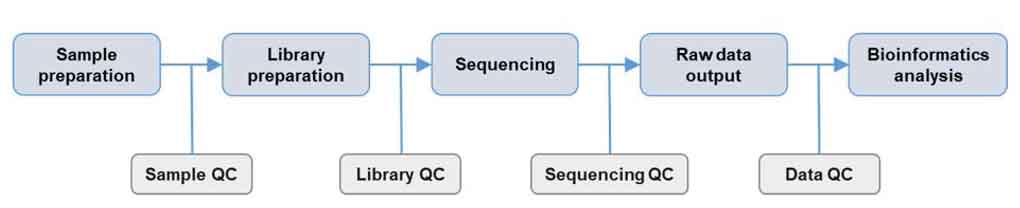
Whole Exome Sequencing (WES)
Whole-exome sequencing (WES) is a genomic technique that sequences only the exons - the protein-coding regions of the genome - which make up about 1-2% of the human genome but contain the majority of known disease-causing mutations. By targeting these regions, WES provides a cost-effective and efficient way to identify genetic variants associated with inherited disorders, cancers, and other diseases. The process involves capturing exonic DNA, sequencing it, and analyzing the data to detect mutations or variants. By only sequencing these protein-coding regions, WES sequencing is much more cost-effective compared to whole-genome sequencing (WGS). Whole-exome sequencing is a powerful method for identifying genetic variants linked to various genetic diseases.
Sample submission requirements
| Service | Sample Type | Recommend Amount | Minimum Amount | Minimum Concentration | Optimal Quality |
| Wes | DNA | 1ug | 100 ng | 10 ng/ul | OD260/OD230 Ratio around 2 |
- Please provide the DNA in nuclease-free water. If any RNase is detected when running DNA chip in our Bioanalyzer 2100, the cost of cleaning up the contamination caused by RNase will be charged.
- Concentration must be measured by Qubit
- This service works only for human samples
- The core has the right to determine if the samples are qualified for the experiment
- Please contact the core via email at [email protected] or call 713-500-7933 for more information.
Service workflow